Hyperglycemia causes changes in the body that make it harder to heal wounds.
Diabetes is a complex health challenge that affects more than 34 million people in the United States.
In addition to an increased risk of developing serious conditions like heart disease, stroke, and kidney failure, people with diabetes are also at higher risk of developing wounds.
In fact, an estimated 15% of diabetics will develop a wound…And about 6% of those patients will require hospitalization due to infection and other wound complications.
An important way to reduce this risk and promote wound healing is to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
What is Hyperglycemia?
Hyperglycemia occurs when there are elevated levels of glucose in the bloodstream. In diabetes, this is caused by either a lack of insulin or when the body is unable to correctly utilize insulin.
Other conditions that may increase blood sugar levels include:
- Dehydration
- Pain
- Stress
- Illness
- Some medications
One common test used to monitor blood glucose levels is hemoglobin A1C, or glycated hemoglobin. This blood test reflects blood glucose control over a 2-3 month period. According to the ADA, a result below 5.7% is considered normal, while the goal for adults with diabetes is to be below 7%.

High Blood Sugar and Wound Healing
Glycemic, or blood sugar, control is an important component of wound healing. When blood glucose levels are high, the body uses proteins and fats for fuel. This results in slower wound healing due to the lack of available protein required to rebuild the damaged tissue.
High glucose levels also cause changes within the cells and arteries that present a challenge for wound healing.

Blood vessels narrow, arteries become more rigid, and red blood cells are not as effective at transporting hemoglobin. These cellular and vascular changes result in decreased delivery of nutrients and oxygen required for healing.
Hyperglycemia Disrupts the Phases of Healing
Hyperglycemia affects every phase of wound healing and disrupts the normal cascade of events needed for tissue repair. As a result of this prolonged process, wounds may become chronic and increasingly difficult to heal.
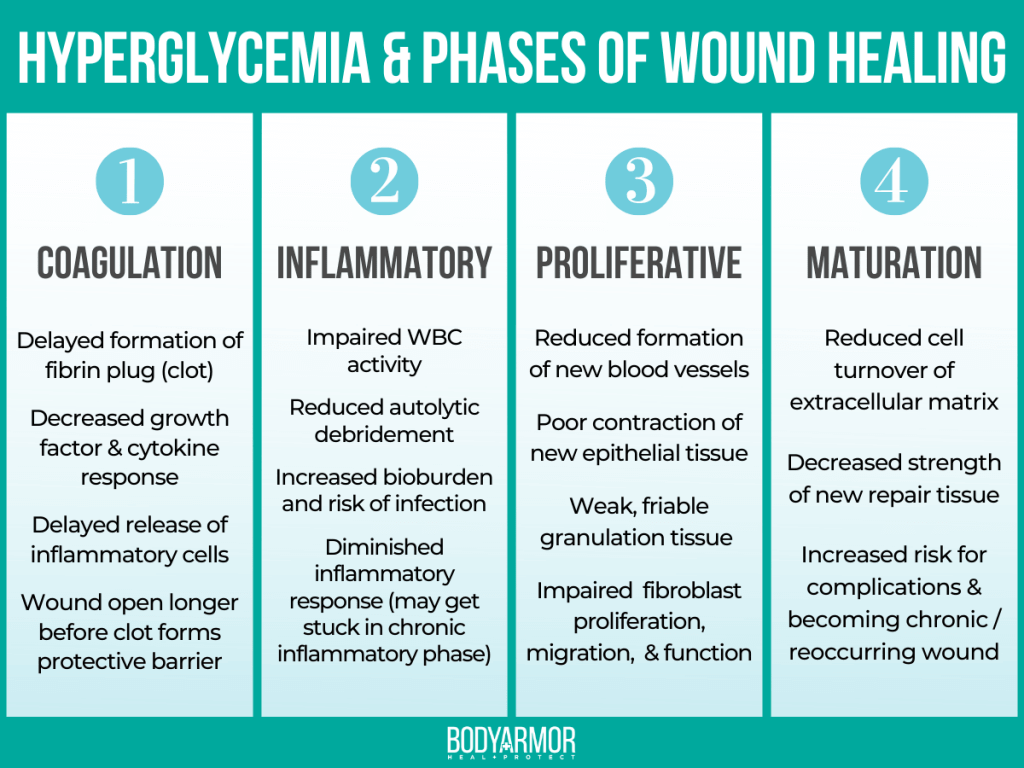
Research shows that careful glycemic control improves the rate of wound healing and reduces complications.
A 2013 study found that patients with elevated A1C or high blood glucose levels around the time of surgery were at over 3 times greater risk of experiencing serious wound complications.
Hyperglycemia and Immune Function
In addition to disrupting the phases of wound healing, hyperglycemia also weakens the immune system’s ability to manage inflammation and fight off infections.
Chronically elevated blood glucose levels cause the body produce several enzymes and hormones that interfere with immune function. Studies have also shown that hyperglycemia impairs the activity of lymphocytes and other important immune cells.
It’s important for people with diabetes to maintain stable blood sugar levels in order to support immune function and reduce the risk of infections.
Steps You Can Take to Promote Wound Healing
- Follow your doctor’s dietary recommendations and medication regimen
- Stay active by engaging in moderate exercise regularly
- Check your skin daily and notify your physician immediately of any new wounds
BODYARMOR Medical Supply Co. Was Founded By Physicians To Make Professional Wound Care Dressings Accessible and Affordable.
Click Here To Explore Our Wound Care Dressings!