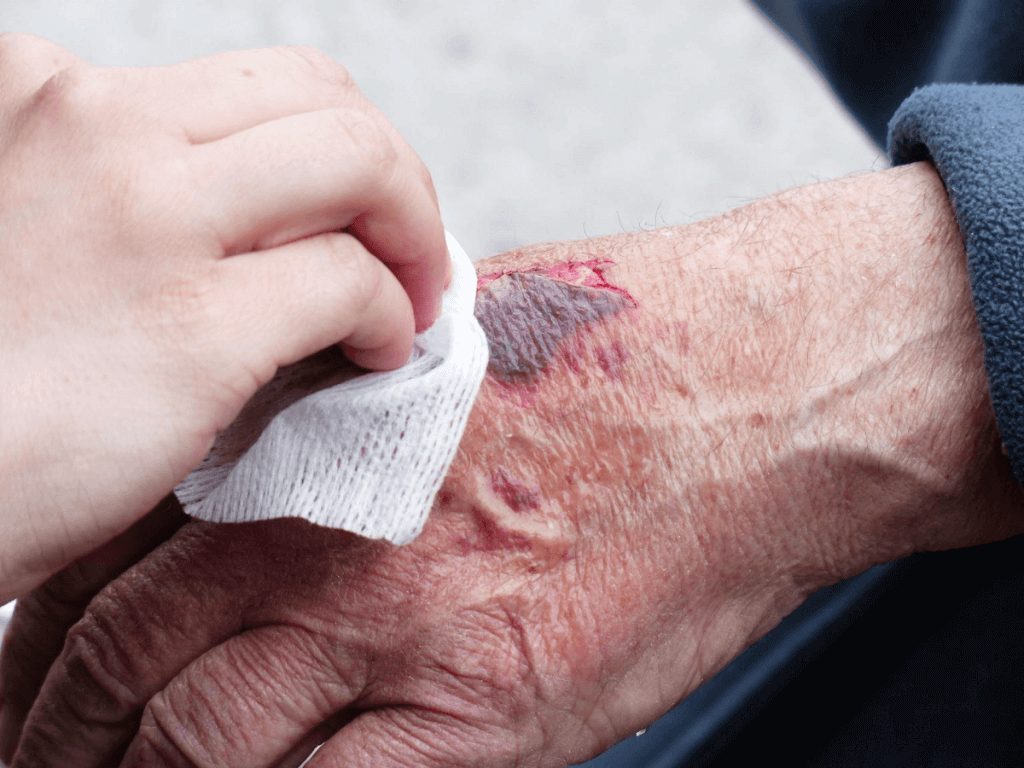
Skin tears are painful, traumatic wounds that occur most often on the arms or legs of older adults.
What causes skin tears?
Skin tears are caused by friction, shearing forces, or blunt trauma against fragile skin. Older adults are more vulnerable to these traumatic injuries due to changes in the layers of the skin with aging.

As the name suggests, these injuries look as if outer layer of the skin has been torn, or peeled back, from the underlying layers.
Common culprits of skin tears include bumping the extremities on equipment or furniture during transfers, rubbing of clothing against the skin, and even improper removal of adhesives or tape.
How long does it take a skin tear to heal?
Depending on the severity of the injury, skin tears can take anywhere from days to weeks to heal. When only the top layer of skin (the epidermis) is separated from the lower layer (the dermis), the injury is considered a partial thickness skin tear.
However, if both the epidermis and dermis have been torn from the underlying layers, the skin tear is classified as full-thickness. This deeper injury typically requires more time to resolve, which increases the risk of complications.
10 Tips for Skin Tear Prevention
Skin tear prevention starts with ensuring your environment is as safe as possible. Follow these 10 simple steps to prevent painful skin tears and keep your skin strong!
#1 – Wear Protective Clothing
Long sleeves, pants, and even socks can act as a barrier between fragile skin and potential forces of friction. Wearing just one extra layer of clothing can significantly reduce trauma during transfers and repositioning compared to bare skin.
#2 – Keep the Room Well-Lit
A poorly lit environment can lead to accidents like missing steps or bumping into furniture. Be sure there is enough lighting for safe movement during the day and at night, and that all cords are secured and out of the way.

#3 – Apply Padding to Equipment & Furniture
Keep walking paths clear of obstructions and use towels or cushions to pad areas of equipment that may be in contact with the skin. Pay special attention to leg rests, wheelchair arms, and any sharp corners of tables and chairs.
#4 – Support Skin Health with Good Nutrition
Eat a balanced diet to keep tissues strong and reduce the risk of breakdown. Be sure to incorporate a variety of fresh fruits, vegetables, and protein sources that include the key vitamins for skin health.
#5 – Keep the Body & Skin Hydrated
Drink plenty of water between meals to maintain good hydration status. This supports skin function, elasticity, and strength – making tissues less susceptible to traumatic injury.

#6 – Avoid Zippers and Other Sharp Closures
Clothing accents such as zippers, beads, and buttons can easily snag on the skin during movement. If these embellishments can’t be avoided completely, it’s best to wear an extra layer underneath and to use extra caution when changing.
#7 – Apply Moisturizing Lotion
Use a fragrance-free moisturizing lotion several times a day, especially on the arms, legs, and any dry areas. Keeping the skin moisturized helps to prevent skin tears, since dry skin is more susceptible to breakdown.

#8 – Move with Slow, Smooth Motions
Focus on using controlled, smooth movements to transfer and reposition. Allow enough time to complete these activities without feeling rushed, and be sure that additional assistance is available if needed.
#9 – Use Non-Adherent Wound Dressings
Some strong tapes and adhesive dressings may pull at the skin and cause trauma upon removal. If an adherent wound dressing is required, opt for a gentle option and remove with the “low and slow” method. (see below!)

#10 – Protect Areas of Fragile Skin
Fragile skin in areas of repeated rubbing or pressure and previous wound sites are some of the areas at the greatest risk of skin tears.
Hydrocolloids may be appropriate over intact skin in areas prone to friction (such as the edges of incontinence briefs) and foams may be used to cushion fragile, healed wound sites (always consult your physician before implementing any wound care treatments).
BODYARMOR Medical Supply Co. Was Founded By Physicians to Make
Professional Wound Care Dressings Accessible and Affordable.
Click Here To Explore Our Wound Care Dressings!